Flowchart Maker: So you need to visualize your processes, right? Whether you’re mapping out a complex project, simplifying a convoluted workflow, or just trying to avoid that dreaded “spaghetti code” situation, flowchart makers are your new best friend. This deep dive explores everything from the market’s hottest players and the latest tech trends to user experience, security concerns, and even a peek into the future of flowcharting.
Get ready to level up your diagramming game!
We’ll cover the core functionalities you should expect, highlight the killer features that set the best ones apart, and show you how to pick a tool that perfectly fits your needs and budget. Think of this as your ultimate guide to navigating the world of flowchart creation – from beginner to pro.
Popularity and Market Trends of Flowchart Makers
The flowchart maker market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for visual communication and process optimization across various industries. From software development to project management, flowcharts provide a clear and concise way to represent complex information, making them an indispensable tool for many professionals. Understanding the market trends and popularity of different flowchart makers is crucial for both users and developers in this space.
Market Share of Top Flowchart Maker Software
Precise market share data for flowchart makers is difficult to obtain due to the fragmented nature of the market and the lack of comprehensive public reporting. However, based on user reviews, online presence, and industry estimations, we can identify some leading players. Lucidchart, draw.io (now diagrams.net), and Microsoft Visio are consistently ranked among the top contenders, followed by other strong players like Creately and Miro.
Determining exact percentages is challenging without access to proprietary market research data. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with newer tools and features constantly emerging.
Growth Trajectory of the Flowchart Maker Market
The flowchart maker market has demonstrated robust growth over the past five years. This growth is fueled by several factors, including the rising adoption of agile methodologies, increased remote work, and the growing need for efficient process management in organizations of all sizes. While precise numerical data requires paid market research reports, anecdotal evidence and industry analyses suggest a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the range of 8-12% over the past five years.
This growth is expected to continue as businesses increasingly rely on visual tools for communication and collaboration. For example, the rise of remote work significantly boosted the demand for collaborative online flowcharting tools.
Emerging Trends in Flowchart Maker Technology
Several key trends are shaping the future of flowchart maker technology. AI-powered features, such as automated flowchart generation from text descriptions or code, are gaining traction. Enhanced collaboration capabilities, including real-time co-editing and integrated communication tools, are becoming increasingly important. Integration with other productivity and project management software is another crucial trend, enabling seamless workflow and data transfer.
Finally, the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions is simplifying access, scalability, and collaboration for users. For instance, the integration of flowchart makers with project management platforms like Asana or Jira streamlines workflows and enhances team productivity.
Pricing Models of Different Flowchart Makers
The pricing models for flowchart makers vary significantly depending on the features, user base, and target market. Here’s a comparison of common pricing strategies:
| Flowchart Maker | Free Plan | Paid Plan (per user/month) | Enterprise Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lucidchart | Limited features, watermarks | Varies based on features, typically $8-$15 | Custom quote, volume discounts |
| draw.io (diagrams.net) | Extensive free features, no watermarks | N/A (Self-hosted options available) | N/A (Self-hosted options available) |
| Microsoft Visio | N/A (Subscription-based) | Included in Microsoft 365 plans | Included in Microsoft 365 enterprise plans |
| Creately | Limited features, watermarks | Varies based on features, typically $5-$10 | Custom quote, volume discounts |
Key Features and Functionality of Flowchart Makers
Flowchart makers have evolved from simple diagramming tools to sophisticated platforms offering a range of features to streamline the visualization and communication of processes. Understanding these features is key to selecting the right tool for your needs, whether you’re a student creating a simple algorithm flowchart or a project manager designing complex workflows.Core functionalities revolve around the creation and manipulation of flowchart elements.
Users can add various shapes representing different process steps, decisions, and data inputs/outputs. These shapes are then connected with lines to show the flow of the process. Most tools offer basic shapes like rectangles, diamonds, and circles, with more advanced options providing a wider selection, including specialized shapes for specific processes like database interactions or network diagrams.
Beyond basic shape manipulation, essential functions include text editing, shape resizing and repositioning, and the ability to group elements for easier management of complex diagrams.
Essential Features Differentiating Flowchart Makers
The differences between flowchart makers often lie in the breadth and depth of their features. Some focus on simplicity and ease of use, while others provide extensive customization and advanced functionalities. For example, some tools might offer a limited library of shapes and templates, whereas others boast extensive libraries with industry-specific shapes and pre-built templates for common workflows.
Similarly, some tools prioritize a simple drag-and-drop interface, while others offer more sophisticated features such as layering, custom shape creation, and advanced alignment options. The level of integration with other applications, such as Microsoft Office suite or project management software, also significantly differentiates these tools. A robust search function within the shape library is another crucial differentiator, enabling quick access to specific symbols.
Collaboration Features in Flowchart Makers
In today’s collaborative work environments, the ability to share and co-edit flowcharts is crucial. Many modern flowchart makers offer real-time collaboration features, allowing multiple users to work on the same diagram simultaneously. This can drastically improve efficiency and reduce the time spent on communication and version control. Features such as commenting, version history, and change tracking are also important for maintaining clarity and transparency in collaborative projects.
Imagine a team working on a complex software development project; real-time collaboration ensures everyone is on the same page and can contribute efficiently to the design process. The ability to assign tasks and track progress within the flowchart itself further enhances team collaboration.
Advanced Features in Premium Flowchart Makers
Premium flowchart makers often include advanced features that significantly enhance productivity and workflow efficiency. These can include features such as automated flowchart generation from code or data, integration with business process management (BPM) systems, and the ability to export diagrams in various formats, including high-resolution images, vector graphics, and interactive web pages. Some advanced tools also offer sophisticated data visualization capabilities, allowing users to integrate real-time data into their flowcharts to track progress and identify bottlenecks.
For instance, a premium tool might allow the integration of data from a project management system to automatically update the flowchart’s progress indicators. Another example is the ability to generate reports directly from the flowchart data, providing insights into process efficiency and potential areas for improvement.
User Experience and Interface Design of Flowchart Makers
A great flowchart maker needs more than just the ability to create diagrams; it needs a user interface (UI) that’s intuitive and enjoyable to use. A clunky or confusing interface can quickly derail even the most dedicated user, leading to frustration and ultimately, abandoned projects. The ideal UI should seamlessly blend powerful functionality with an effortless user experience.
The overall goal is to minimize cognitive load and maximize efficiency. Users should be able to focus on the task at hand—creating their flowchart—without getting bogged down in navigating the software itself. This requires careful consideration of every aspect of the design, from the layout and visual elements to the keyboard shortcuts and overall workflow.
Ideal User Interface Design for Ease of Use
The ideal flowchart maker interface should prioritize simplicity and clarity. A clean, uncluttered workspace allows users to focus on their diagrams. Drag-and-drop functionality for shapes and connectors is essential, as is easy access to styling options like colors, fonts, and line thicknesses. A well-organized toolbar, readily accessible menus, and clear visual cues help users quickly find the tools they need.
The software should also offer autosave functionality to prevent accidental data loss. Furthermore, a user-friendly zoom function allows for detailed work on complex diagrams. The ability to easily group and ungroup elements streamlines the workflow for larger, more complex projects. Finally, a robust undo/redo function provides a safety net for those inevitable accidental deletions or edits.
Common Usability Issues in Flowchart Maker Software
Despite the advancements in software design, many flowchart makers still suffer from usability issues. These often stem from a lack of user-centered design practices.
- Overly complex interfaces: Too many buttons, menus, and options can overwhelm users.
- Poorly designed toolbars: Icons that are not intuitive or consistently styled make it difficult to identify tools quickly.
- Lack of visual feedback: Users need clear visual cues to understand the effects of their actions.
- Inconsistent keyboard shortcuts: A lack of consistent keyboard shortcuts makes the software less efficient to use.
- Insufficient zoom functionality: The inability to zoom in and out easily hinders work on large or detailed diagrams.
- Limited undo/redo capabilities: Restricting the undo/redo function makes it harder to recover from mistakes.
- Poor error handling: Vague or unhelpful error messages leave users confused and frustrated.
Comparative Analysis of User Interface Design, Flowchart maker
Let’s compare the UI design of three popular flowchart makers: Lucidchart, draw.io, and Microsoft Visio.
| Feature | Lucidchart | draw.io | Microsoft Visio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Highly intuitive drag-and-drop interface; clean and uncluttered workspace. | Simple and straightforward interface; suitable for beginners. | Steeper learning curve; more features can lead to initial confusion. |
| Toolbar Design | Well-organized and easily accessible toolbar. | Clear and concise toolbar, though some features are nested within menus. | More complex toolbar with many features; can feel overwhelming for new users. |
| Visual Feedback | Excellent visual feedback during drag-and-drop operations and shape manipulation. | Provides adequate visual feedback, though could be improved in certain areas. | Visual feedback is generally good, but some aspects could be more intuitive. |
| Zoom Functionality | Seamless zoom functionality; allows for easy navigation of large diagrams. | Good zoom functionality; works effectively for most use cases. | Zoom functionality is present but could be more responsive. |
Intuitive Navigation and User Experience
Intuitive navigation significantly improves the user experience. Features like drag-and-drop, context menus (right-click menus that offer actions relevant to the selected element), and keyboard shortcuts allow for rapid creation and manipulation of flowchart elements. For example, the ability to instantly connect shapes with a simple drag-and-drop action, rather than navigating through menus, drastically reduces the time and effort required to build a flowchart.
Clear visual cues, such as highlighting connected elements or providing real-time feedback on shape alignment, further enhance the user’s understanding of the diagram’s structure and prevent errors. A well-designed interface anticipates user needs, providing easy access to frequently used tools and minimizing the need for extensive searching or menu navigation. This streamlined workflow allows users to concentrate on the content and logic of their flowchart rather than the mechanics of the software.
Integration Capabilities of Flowchart Makers
Flowchart makers aren’t just standalone apps; their real power lies in their ability to seamlessly integrate with your existing workflow. This integration boosts productivity by eliminating data silos and streamlining the process of creating, sharing, and collaborating on flowcharts. Effective integration allows you to easily move your flowchart data between different applications, saving time and minimizing errors.Integrating a flowchart maker with other productivity software enhances its usefulness considerably.
The ability to link flowcharts directly with project management tools, communication platforms, and other business applications simplifies workflows and fosters better collaboration. This interoperability is a key factor in choosing a flowchart maker, especially for teams and businesses.
Project Management Tool Integrations
Many popular flowchart makers offer direct integration with leading project management platforms like Asana, Trello, and Jira. This integration typically allows users to link flowchart diagrams to specific tasks or projects within the project management system. For instance, a flowchart detailing a software development process could be directly linked to the corresponding tasks in Jira, providing a visual representation of the workflow and its progress.
This bidirectional link allows updates in one system to reflect in the other, ensuring everyone is on the same page. A drawback of such integrations can be the complexity of setting up the connection and potential synchronization issues if the platforms aren’t properly configured.
Communication Platform Integrations
The ability to easily share and collaborate on flowcharts is crucial. Integrations with communication platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Google Workspace allow for seamless sharing of flowcharts directly within these platforms. This eliminates the need to manually export and upload files, saving time and ensuring everyone has access to the most up-to-date version. However, some integrations might be limited in functionality, only allowing for static image sharing instead of interactive, editable flowcharts.
This limitation can reduce the collaborative potential of the integration.
Integration Methods and Their Benefits and Drawbacks
Different integration methods offer varying levels of functionality and complexity. API-based integrations offer the most flexibility and powerful capabilities, allowing for complex data exchange and automation. However, they require technical expertise to set up and maintain. On the other hand, simpler methods like file import/export or copy-paste are easier to use but offer less flexibility. The best method depends on the specific needs and technical capabilities of the user and the integrated applications.
Flowchart: Integration of Flowchart Maker with Project Management Software
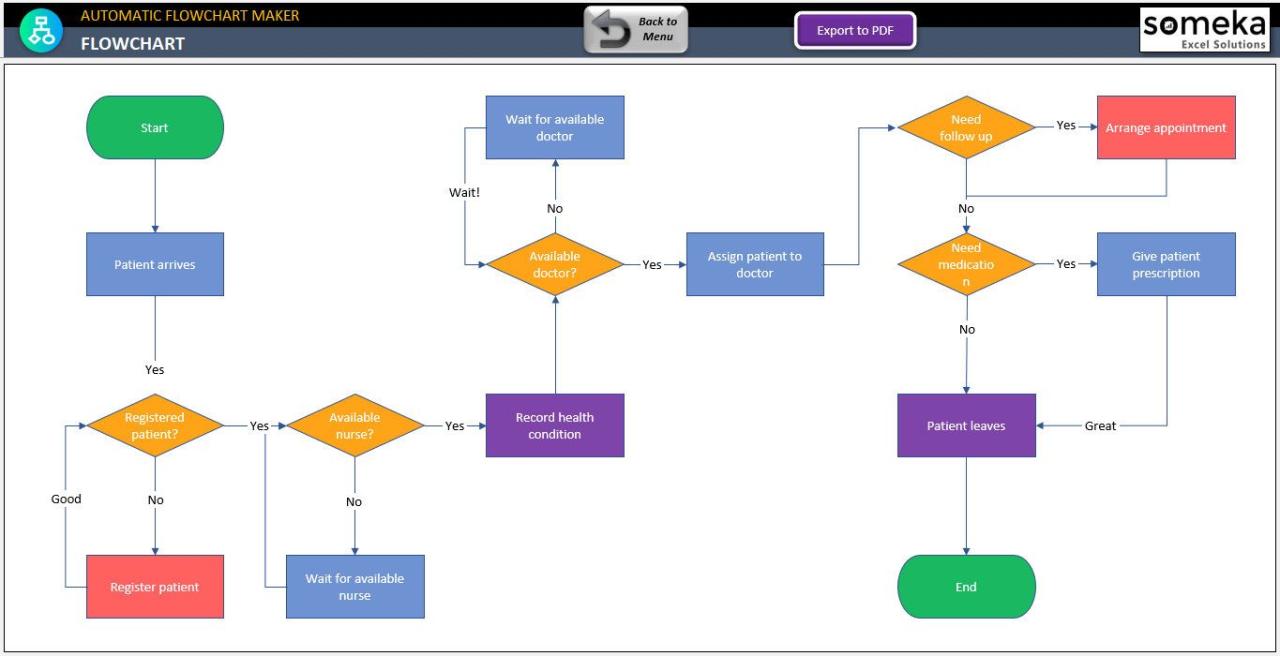
Imagine a flowchart maker integrating with Asana. The flowchart illustrates the process:The flowchart would start with a “Create Flowchart” block. This would lead to a “Select Asana Project” block, where the user chooses a relevant project from their Asana workspace. Next, a “Link Flowchart to Task” block would appear, where the user links the flowchart to a specific task within the chosen Asana project.
Following this, a “Save and Sync” block would initiate the process of saving the flowchart and syncing it with Asana. Finally, an “Asana Task Updated” block would confirm the successful integration and the updated task status within Asana. The flowchart would visually depict this process, highlighting the seamless transfer of data between the flowchart maker and Asana. This visual representation would help users understand the integration process clearly.
A potential additional block could be an “Error Handling” block that deals with any issues during the synchronization process.
Security and Privacy Considerations for Flowchart Makers
Online flowchart makers offer convenience and collaboration, but they also introduce potential security and privacy risks. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is crucial for protecting sensitive information and maintaining confidentiality. This section explores these concerns, focusing on data protection best practices and the security features offered by various platforms.
Potential Security Risks Associated with Online Flowchart Makers
Using online flowchart makers inherently involves entrusting your data to a third-party service. This introduces several potential security risks. Data breaches, unauthorized access, and malicious code injection are all possibilities. The risk level varies depending on the security measures implemented by the provider and the sensitivity of the data being used. For example, a flowchart containing only project planning information presents a lower risk than one detailing sensitive business strategies or personal health information.
Furthermore, the security of the user’s own devices and network infrastructure also plays a crucial role in overall security. Weak passwords, unpatched software, and unsecured networks can create vulnerabilities that compromise even the most secure flowchart maker.
So, you’re making flowcharts, right? Once you’ve got your awesome diagram, you might want to add it to a document. That’s where a solid pdf editor online comes in handy. You can easily insert your flowchart into a PDF, making it super clean and shareable. Then, you can get back to perfecting your flowchart design!
Best Practices for Protecting Data Privacy When Using Flowchart Makers
Protecting data privacy when using online flowchart makers requires a multi-faceted approach. Users should always choose reputable providers with a strong track record of security. Look for providers that offer robust encryption both in transit and at rest. Avoid sharing sensitive data unnecessarily, and utilize access control features to limit who can view and edit your flowcharts.
Employ strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication wherever possible. Regularly review the privacy policies of the flowchart maker you are using to ensure they align with your data protection needs. Finally, consider the sensitivity of the data before uploading it and opt for offline tools if the risk is high.
Data Encryption and Access Control in Flowchart Makers
Data encryption and access control are fundamental security measures for flowchart makers. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the correct decryption key. This protects data both during transmission (in transit) and when stored on the provider’s servers (at rest). Access control mechanisms, such as role-based permissions, allow administrators to granularly control who can view, edit, and share flowcharts.
This prevents unauthorized access and modification of sensitive information. For example, a company might grant only certain employees access to flowcharts containing confidential financial data. Robust implementation of both encryption and access control significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Comparison of Security Measures Implemented by Different Flowchart Makers
Different flowchart makers employ varying security measures. Some offer basic encryption and access control, while others provide more advanced features such as multi-factor authentication, audit trails, and compliance certifications (like ISO 27001 or SOC 2). A thorough comparison of the security features offered by different providers is crucial before selecting a platform. Consider factors such as data location, encryption methods used, access control options, and the provider’s security policies and incident response plan.
For example, a company dealing with highly sensitive data might prioritize a provider with robust security certifications and a transparent security posture over a simpler, less secure option. Ultimately, the choice depends on the specific security requirements and risk tolerance of the user or organization.
Types of Flowcharts Created by Flowchart Makers
Flowchart makers offer a diverse range of flowchart types, each designed for specific purposes and industries. Understanding these different types is crucial for effectively visualizing processes and workflows. The choice of flowchart type depends heavily on the complexity of the process being depicted and the information that needs to be conveyed.
Different flowchart types use varying symbols and conventions to represent different steps, decisions, and data flows. Mastering these conventions is key to creating clear and easily understandable flowcharts. The following sections will explore some of the most common types, their applications, and the process of creating them using a flowchart maker.
Basic Flowcharts
Basic flowcharts are the most fundamental type, suitable for illustrating simple processes with a linear sequence of steps. They’re often used for introductory programming concepts or simple business processes. These flowcharts primarily utilize rectangular boxes for processes, diamonds for decisions, and arrows to indicate the flow of the process.
For example, a basic flowchart could depict the process of making a cup of coffee: start, boil water, add coffee grounds, brew, pour, enjoy, end. Each step would be represented by a rectangle, with arrows connecting them to show the sequence. In manufacturing, a basic flowchart might Artikel the assembly steps for a simple product.
Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
Data flow diagrams focus on the flow of data within a system. They’re commonly used in software engineering and system analysis to model data movement and transformation. DFDs use specific symbols to represent processes, data stores, data flows, and external entities.
Imagine designing a new e-commerce website. A DFD would illustrate how customer data flows from the order placement to the database, then to the inventory management system, and finally to the shipping department. The symbols used might include circles for processes, open-ended rectangles for data stores, and arrows labeled with data names to represent data flows.
Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams, also known as cross-functional flowcharts, are used to show the responsibilities of different actors or departments within a process. Each “swimlane” represents a different actor or department, and the steps are arranged within their respective lanes. This makes it easy to see who is responsible for each step and identify potential bottlenecks or areas for improvement.
A hospital’s patient admission process could be effectively illustrated using a swimlane diagram. One lane might represent the reception desk, another the doctor, another the billing department, and so on. Each step in the admission process would be placed within the appropriate lane, showing the handoff between different departments.
UML Activity Diagrams
UML (Unified Modeling Language) activity diagrams are more complex than basic flowcharts and are used to model the flow of control in a system or process. They are particularly useful for representing complex business processes or software workflows. They use a variety of symbols, including action states, decision nodes, and merge nodes, to represent different aspects of the process.
Consider the process of online banking. A UML activity diagram would model the flow of events from logging in, to transferring funds, to confirming the transaction, and finally logging out. The diagram would use specialized UML symbols to represent actions, decisions, and parallel processes, providing a more detailed and comprehensive representation than a simple flowchart.
Creating a Flowchart using a Flowchart Maker
The process of creating a flowchart using a flowchart maker typically involves these steps:
- Selecting the appropriate flowchart type.
- Adding shapes and connectors to represent the steps and decisions in the process.
- Labeling shapes with clear and concise descriptions.
- Connecting shapes with arrows to show the flow of the process.
- Reviewing and refining the flowchart for clarity and accuracy.
- Exporting the flowchart in the desired format (e.g., image, PDF).
Most flowchart makers offer drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built shapes, simplifying the creation process.
Cost-Effectiveness and Value for Money of Flowchart Makers
Choosing the right flowchart maker involves careful consideration of its cost against the benefits it provides. Different tools offer varying feature sets at different price points, making a direct comparison crucial for maximizing your investment. This section examines the pricing structures, return on investment, and influential factors impacting the cost-effectiveness of various flowchart makers.
Pricing Models of Flowchart Makers
Flowchart makers typically employ several pricing models. Free plans often offer limited features and functionality, suitable for occasional users or small projects. Subscription-based models provide access to a wider range of tools and features, often with tiered pricing reflecting the level of access and support. One-time purchase models are less common but might offer a complete suite of tools at a fixed cost.
Some providers may also offer customized enterprise solutions with tailored pricing based on specific organizational needs. Understanding these different models is key to finding the best fit for your budget and workflow.
Return on Investment (ROI) of Using a Flowchart Maker
The ROI of a flowchart maker is multifaceted. Improved team communication, reduced project ambiguity, streamlined workflows, and enhanced efficiency all contribute to a positive ROI. By visualizing processes, flowchart makers help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, leading to cost savings in time and resources. For example, a company using a flowchart maker to design a new product launch process might reduce errors and rework, leading to significant cost savings compared to a manual approach.
Quantifying these benefits may require careful tracking of time saved, reduced errors, and improved project completion rates.
Factors Influencing the Cost-Effectiveness of a Flowchart Maker
Several factors influence the cost-effectiveness of a flowchart maker. The complexity of your projects, the number of users, the required level of collaboration features, and the importance of integration with other software all play a role. A simple, free tool might suffice for personal use or small, straightforward projects, while a more sophisticated, paid tool may be necessary for complex projects involving multiple teams and extensive collaboration.
The long-term costs, including subscription fees and potential training expenses, should also be considered against the expected benefits.
Pricing and Feature Comparison of Flowchart Makers
The following table summarizes the pricing and key features of some popular flowchart makers. Note that pricing and features are subject to change, so it’s crucial to check the vendor’s website for the most up-to-date information.
| Flowchart Maker | Pricing Model | Key Features | Target User |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lucidchart | Free, individual, team, and enterprise subscriptions | Collaboration tools, extensive shape libraries, integration with other apps | Individuals, teams, and enterprises |
| Draw.io | Free, with paid options for additional features | Large template library, easy-to-use interface, various export options | Individuals and teams |
| Microsoft Visio | One-time purchase or subscription (Microsoft 365) | Advanced diagramming capabilities, integration with Microsoft Office suite | Individuals and enterprises |
| Creately | Free, individual, and team subscriptions | Real-time collaboration, diverse template selection, mobile accessibility | Individuals and teams |
Impact of Flowchart Makers on Productivity and Collaboration
Flowchart makers significantly boost productivity and collaboration within teams by providing a visual and easily understandable representation of processes, workflows, and projects. This visual clarity facilitates better communication, streamlines project planning and execution, and ultimately leads to increased efficiency across various professional settings.Flowchart makers improve team collaboration and communication by offering a shared visual workspace. Team members can collaboratively create, edit, and comment on flowcharts, fostering a shared understanding of the project’s scope, tasks, and dependencies.
This shared visual language minimizes ambiguity and reduces the likelihood of miscommunication, leading to smoother workflows and a more unified team effort. The ability to leave comments directly on specific flowchart elements further enhances communication, making feedback and suggestions precise and targeted.
Improved Project Planning and Execution
Using flowchart makers during the project planning phase allows teams to clearly define project scope, identify critical path tasks, and allocate resources effectively. The visual representation helps to uncover potential bottlenecks and dependencies early on, enabling proactive mitigation strategies. During project execution, the flowchart acts as a roadmap, keeping the team focused on tasks and deadlines. Regular updates to the flowchart reflect progress and highlight any deviations from the plan, allowing for timely adjustments and course correction.
For example, a software development team using a flowchart maker can visualize the dependencies between different coding modules, identify potential integration issues early, and allocate developer resources more effectively. This reduces development time and improves the overall quality of the software.
Increased Workplace Productivity
Flowchart makers contribute to increased workplace productivity by streamlining workflows, reducing errors, and improving decision-making. The visual representation of processes allows for quick identification of inefficiencies and areas for improvement. By clearly outlining steps and responsibilities, flowcharts minimize confusion and reduce the time spent on clarifying tasks or resolving misunderstandings. This clear visualization enables teams to focus their efforts on completing tasks rather than deciphering complex instructions or resolving ambiguities.
The result is a significant increase in overall productivity and efficiency.
Real-World Examples of Efficiency Improvements
Consider a hospital using a flowchart maker to map out patient intake procedures. By visualizing the process, they identified redundancies and bottlenecks, leading to a reduction in patient wait times and improved efficiency. Similarly, a manufacturing company using a flowchart maker to visualize its production line identified areas where automation could be implemented, leading to increased output and reduced production costs.
In the education sector, instructors can use flowcharts to visualize lesson plans, making the learning process more structured and easier for students to follow. This clear visualization helps students understand the learning objectives and the steps involved in achieving them, leading to improved learning outcomes.
Future Directions and Innovations in Flowchart Maker Technology
Flowchart maker technology is poised for significant advancements, driven by the increasing demand for visual communication tools and the rapid evolution of related technologies. We can expect to see increasingly sophisticated software, incorporating AI and other innovations, that dramatically improve the creation, sharing, and analysis of flowcharts.The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) will be a key driver of future developments.
This will lead to more intuitive and efficient tools, allowing users to create complex flowcharts with minimal effort. Beyond simple automation, AI will allow for more intelligent features, including automatic flowchart generation from text descriptions or code, and advanced analysis capabilities to identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies within the visualized processes.
AI-Powered Features in Flowchart Makers
AI will revolutionize several aspects of flowchart creation. For example, imagine a system that can automatically convert a natural language description of a process – such as “The customer submits a request, then it’s reviewed by a manager, and finally processed by the support team” – directly into a visually appealing and accurate flowchart. Another powerful application would be AI-driven analysis of existing flowcharts, highlighting potential problems such as redundant steps or unnecessary complexities.
This could be particularly valuable for large, intricate processes where manual analysis is time-consuming and prone to error. Think of a manufacturing process with hundreds of steps – AI could quickly pinpoint areas for improvement that a human might overlook. Furthermore, AI could personalize the user experience by suggesting optimal flowchart layouts based on the user’s past creations and project context.
Predictive Modeling and Enhanced Collaboration in Flowchart Makers
Future flowchart makers will likely incorporate predictive modeling capabilities. This means the software could anticipate user needs and suggest relevant shapes, connectors, or even entire flowchart segments based on the context of the project. For example, if a user is creating a flowchart for a software development process, the software could automatically suggest shapes representing different coding stages or testing phases.
Simultaneously, enhanced collaboration features, potentially incorporating real-time co-editing and version control similar to document collaboration platforms, will become increasingly prevalent. This will allow teams to work together seamlessly on complex flowcharts, regardless of their geographical location. Imagine a global team collaboratively refining a manufacturing process flowchart in real-time, with integrated commenting and version history to track changes and facilitate efficient communication.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Flowchart Maker Design
The integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies presents exciting possibilities. AR could overlay flowchart elements onto real-world environments, providing a more immersive and intuitive design experience. For example, a user could visualize a manufacturing process flowchart superimposed onto the actual factory floor. VR could create fully immersive environments for collaborative flowchart design, allowing team members to interact with the flowchart in a three-dimensional space.
Additionally, the increasing adoption of cloud computing will allow for enhanced scalability, accessibility, and collaboration features. Cloud-based flowchart makers will allow users to access their diagrams from anywhere with an internet connection, and will facilitate seamless collaboration amongst team members. Finally, the continued development of improved rendering engines and user interface designs will lead to more visually appealing and user-friendly flowchart makers, with intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces and support for a wider range of customization options.
Case Studies of Successful Flowchart Maker Implementations
Implementing a flowchart maker can significantly boost a company’s operational efficiency and streamline workflows. The success of such implementations, however, depends on careful planning, user training, and a clear understanding of the company’s specific needs. This section will examine a case study illustrating both the benefits and challenges associated with integrating a flowchart maker into a business environment.
Case Study: Acme Corporation’s Implementation of “FlowPro”
Acme Corporation, a mid-sized manufacturing company, faced significant challenges in managing its complex production processes. Their existing system relied heavily on outdated documentation and informal communication, leading to frequent errors, bottlenecks, and delays. To address these issues, they decided to implement FlowPro, a cloud-based flowcharting software. The implementation involved a phased rollout, beginning with a pilot program in the production planning department.
This allowed the company to test the software’s functionality, identify potential issues, and refine their implementation strategy before expanding its use across other departments.
Benefits Experienced During Implementation
The initial rollout of FlowPro in the production planning department yielded immediate benefits. The ability to visually represent complex processes facilitated better understanding and communication among team members. This led to a reduction in errors and improved collaboration. The software’s version control features also helped maintain process documentation accuracy, eliminating the confusion caused by outdated or conflicting information.
Furthermore, FlowPro’s reporting capabilities provided valuable insights into production bottlenecks, allowing for more efficient resource allocation and process optimization. The company also noted a significant decrease in the time spent on documentation and process updates.
Challenges Encountered During Implementation
Despite the overall success of the implementation, Acme Corporation faced several challenges. The initial training phase required significant time and resources. Some employees were initially resistant to adopting new software, requiring additional support and encouragement. Integration with existing enterprise systems also proved more complex than initially anticipated, requiring custom scripting and adjustments. Finally, the company had to address concerns regarding data security and privacy, implementing robust access controls and encryption protocols to ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Improvements to Workflow and Efficiency
Following the successful pilot program, Acme Corporation expanded the use of FlowPro across other departments, including quality control, supply chain management, and customer service. The consistent use of visual process maps improved communication and collaboration across departments, reducing misunderstandings and delays. The ability to easily update and share process diagrams ensured everyone worked with the most current information.
This improved efficiency translated into significant cost savings and increased productivity, with measurable improvements in on-time delivery and reduced production errors.
Key Takeaways from Acme Corporation’s FlowPro Implementation
| Aspect | Benefit | Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process Visualization | Improved communication and understanding of complex processes. | Initial resistance to adopting new software. | Comprehensive training and ongoing support. |
| Collaboration | Enhanced teamwork and reduced errors due to improved communication. | Integration with existing systems. | Custom scripting and IT support. |
| Efficiency | Significant reduction in time spent on documentation and process updates. Improved resource allocation. | Data security and privacy concerns. | Robust access controls and encryption. |
| Cost Savings | Measurable improvements in on-time delivery and reduced production errors. | Initial investment in software and training. | Phased rollout and ROI analysis. |
Conclusive Thoughts
From market trends to future innovations, we’ve covered the essential aspects of flowchart makers. Ultimately, the right tool depends on your specific needs and preferences. Consider your budget, required features, and desired level of integration when making your choice. But remember, a well-chosen flowchart maker can significantly boost your productivity, improve team collaboration, and make even the most complicated projects seem manageable.
So ditch the sticky notes and embrace the power of visual organization!
Quick FAQs: Flowchart Maker
What file formats do flowchart makers typically support?
Most flowchart makers support common image formats like PNG, JPG, and SVG, as well as their own proprietary formats for easy editing and sharing. Some also offer export options to PDF and other document formats.
Are there free flowchart maker options available?
Yes, several free flowchart makers exist, often with limitations on features or the number of diagrams you can create. Paid versions usually unlock advanced features and remove limitations.
Can I collaborate on flowcharts in real-time?
Many modern flowchart makers offer real-time collaboration features, allowing multiple users to work on the same diagram simultaneously. This is particularly useful for teamwork and project management.
How do I choose the best flowchart maker for my needs?
Consider factors like your budget, the complexity of your diagrams, required features (e.g., collaboration, integrations), and the user interface’s ease of use. Try out free trials or demos before committing to a paid subscription.
What are the security implications of using cloud-based flowchart makers?
Cloud-based flowchart makers may present security risks if the provider doesn’t have robust security measures. Look for providers with strong encryption, access controls, and a clear privacy policy before storing sensitive data.
